Machine Learning Interview Questions
 Learn via Video Course
Learn via Video Course
 Learn via Video Course
Learn via Video Course
Introduction
This page will guide you to brush up on the skills of machine learning to crack the interview.
Here, our focus will be on real-world scenario ML interview questions asked in Microsoft, Amazon, etc., And how to answer them.
Let’s get started!
Firstly, Machine Learning refers to the process of training a computer program to build a statistical model based on data. The goal of machine learning (ML) is to turn data and identify the key patterns out of data or to get key insights.
For example, if we have a historical dataset of actual sales figures, we can train machine learning models to predict sales for the coming future.
Why is the Machine Learning trend emerging so fast?
Machine Learning solves Real-World problems. Unlike the hard coding rule to solve the problem, machine learning algorithms learn from the data.
The learnings can later be used to predict the feature. It is paying off for early adopters.
A full 82% of enterprises adopting machine learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) have gained a significant financial advantage from their investments.
According to Deloitte, companies have an impressive median ROI of 17%.
Machine Learning Interview Questions For Freshers
1. Why was Machine Learning Introduced?
The simplest answer is to make our lives easier. In the early days of “intelligent” applications, many systems used hardcoded rules of “if” and “else” decisions to process data or adjust the user input. Think of a spam filter whose job is to move the appropriate incoming email messages to a spam folder.
But with the machine learning algorithms, we are given ample information for the data to learn and identify the patterns from the data.
Unlike the normal problems we don’t need to write the new rules for each problem in machine learning, we just need to use the same workflow but with a different dataset.
Let’s talk about Alan Turing, in his 1950 paper, “Computing Machinery and Intelligence”, Alan asked, “Can machines think?”
Full paper here
The paper describes the “Imitation Game”, which includes three participants -
- Human acting as a judge,
- Another human, and
- A computer is an attempt to convince the judge that it is human.
The judge asks the other two participants to talk. While they respond the judge needs to decide which response came from the computer. If the judge could not tell the difference the computer won the game.
The test continues today as an annual competition in artificial intelligence. The aim is simple enough: convince the judge that they are chatting to a human instead of a computer chatbot program.


 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Prep for Target Roles
Prep for Target Roles
 Custom Plan Duration
Custom Plan Duration
 Flexible Plans
Flexible Plans
2. What are Different Types of Machine Learning algorithms?
There are various types of machine learning algorithms. Here is the list of them in a broad category based on:
- Whether they are trained with human supervision (Supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement learning)
- The criteria in the below diagram are not exclusive, we can combine them any way we like.

3. What is Supervised Learning?
Supervised learning is a machine learning algorithm of inferring a function from labeled training data. The training data consists of a set of training examples.
Example: 01
Knowing the height and weight identifying the gender of the person. Below are the popular supervised learning algorithms.
- Support Vector Machines
- Regression
- Naive Bayes
- Decision Trees
- K-nearest Neighbour Algorithm and Neural Networks.
Example: 02
If you build a T-shirt classifier, the labels will be “this is an S, this is an M and this is L”, based on showing the classifier examples of S, M, and L.
4. What is Unsupervised Learning?
Unsupervised learning is also a type of machine learning algorithm used to find patterns on the set of data given. In this, we don’t have any dependent variable or label to predict. Unsupervised Learning Algorithms:
- Clustering,
- Anomaly Detection,
- Neural Networks and Latent Variable Models.
Example:
In the same example, a T-shirt clustering will categorize as “collar style and V neck style”, “crew neck style” and “sleeve types”.
5. What is ‘Naive’ in a Naive Bayes?
The Naive Bayes method is a supervised learning algorithm, it is naive since it makes assumptions by applying Bayes’ theorem that all attributes are independent of each other.
Bayes’ theorem states the following relationship, given class variable y and dependent vector x1 through xn:
P(yi | x1,..., xn) =P(yi)P(x1,..., xn | yi)(P(x1,..., xn)
Using the naive conditional independence assumption that each xiis independent: for all I this relationship is simplified to:
P(xi | yi, x1, ..., xi-1, xi+1, ...., xn) = P(xi | yi)
Since, P(x1,..., xn) is a constant given the input, we can use the following classification rule:
P(yi | x1, ..., xn) = P(y) ni=1P(xi | yi)P(x1,...,xn) and we can also use Maximum A Posteriori (MAP) estimation to estimate P(yi)and P(yi | xi) the former is then the relative frequency of class yin the training set.
P(yi | x1,..., xn) P(yi) ni=1P(xi | yi)
y = arg max P(yi)ni=1P(xi | yi)
The different naive Bayes classifiers mainly differ by the assumptions they make regarding the distribution of P(yi | xi): can be Bernoulli, binomial, Gaussian, and so on.
 Learn via our Video Courses
Learn via our Video Courses
6. What is PCA? When do you use it?
Principal component analysis (PCA) is most commonly used for dimension reduction.
In this case, PCA measures the variation in each variable (or column in the table). If there is little variation, it throws the variable out, as illustrated in the figure below:

Thus making the dataset easier to visualize. PCA is used in finance, neuroscience, and pharmacology.
It is very useful as a preprocessing step, especially when there are linear correlations between features.
7. Explain SVM Algorithm in Detail
A Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a very powerful and versatile supervised machine learning model, capable of performing linear or non-linear classification, regression, and even outlier detection.
Suppose we have given some data points that each belong to one of two classes, and the goal is to separate two classes based on a set of examples.
In SVM, a data point is viewed as a p-dimensional vector (a list of p numbers), and we wanted to know whether we can separate such points with a (p-1)-dimensional hyperplane. This is called a linear classifier.
There are many hyperplanes that classify the data. To choose the best hyperplane that represents the largest separation or margin between the two classes.
If such a hyperplane exists, it is known as a maximum-margin hyperplane and the linear classifier it defines is known as a maximum margin classifier. The best hyperplane that divides the data in H3
We have data (x1, y1), ..., (xn, yn), and different features (xii, ..., xip), and yiis either 1 or -1.
The equation of the hyperplane H3 is the set of points satisfying:
w. x-b = 0
Where w is the normal vector of the hyperplane. The parameter b||w||determines the offset of the hyperplane from the original along the normal vector w
So for each i, either xiis in the hyperplane of 1 or -1. Basically, xisatisfies:
w . xi - b = 1 or w. xi - b = -1



 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Detailed reports
Detailed reports
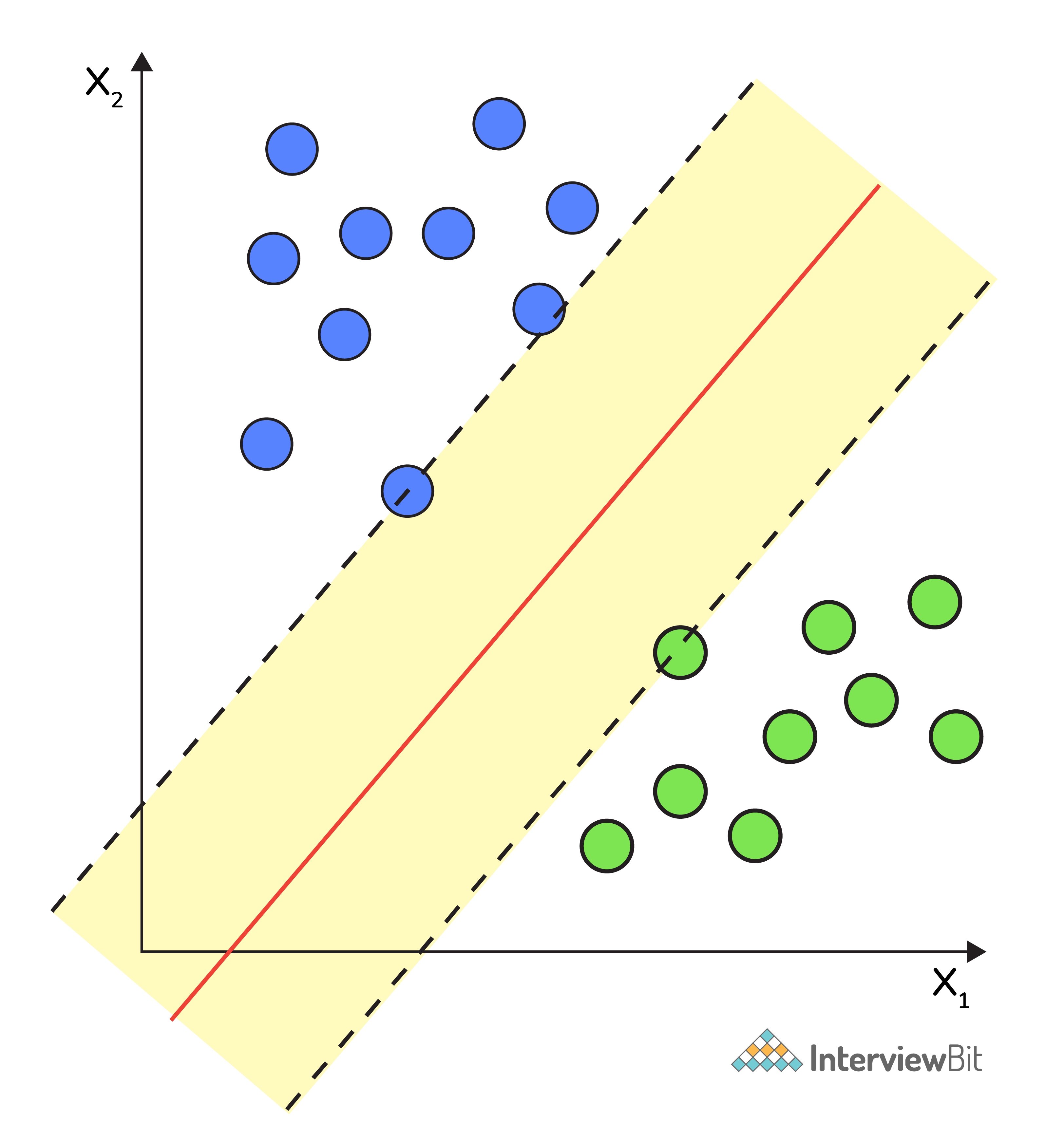
8. What are Support Vectors in SVM?
A Support Vector Machine (SVM) is an algorithm that tries to fit a line (or plane or hyperplane) between the different classes that maximizes the distance from the line to the points of the classes.
In this way, it tries to find a robust separation between the classes. The Support Vectors are the points of the edge of the dividing hyperplane as in the below figure.
9. What are Different Kernels in SVM?
There are six types of kernels in SVM:
- Linear kernel - used when data is linearly separable.
- Polynomial kernel - When you have discrete data that has no natural notion of smoothness.
- Radial basis kernel - Create a decision boundary able to do a much better job of separating two classes than the linear kernel.
- Sigmoid kernel - used as an activation function for neural networks.
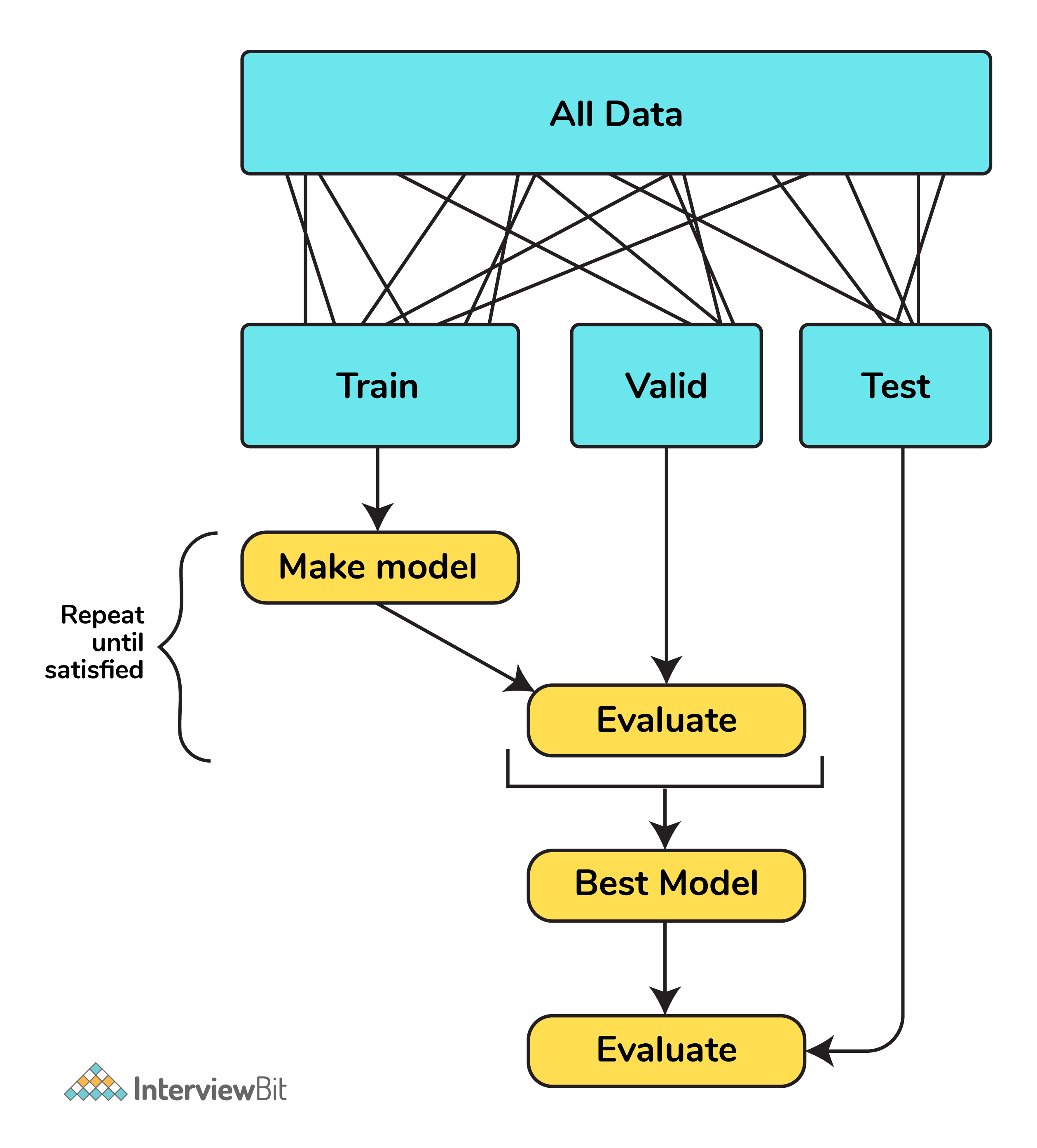
10. What is Cross-Validation?
Cross-validation is a method of splitting all your data into three parts: training, testing, and validation data. Data is split into k subsets, and the model has trained on k-1of those datasets.
The last subset is held for testing. This is done for each of the subsets. This is k-fold cross-validation. Finally, the scores from all the k-folds are averaged to produce the final score.
11. What is Bias in Machine Learning?
Bias in data tells us there is inconsistency in data. The inconsistency may occur for several reasons which are not mutually exclusive.
For example, a tech giant like Amazon to speed the hiring process they build one engine where they are going to give 100 resumes, it will spit out the top five, and hire those.
When the company realized the software was not producing gender-neutral results it was tweaked to remove this bias.
12. Explain the Difference Between Classification and Regression?
Classification is used to produce discrete results, classification is used to classify data into some specific categories.
For example, classifying emails into spam and non-spam categories.
Whereas, regression deals with continuous data.
For example, predicting stock prices at a certain point in time.
Classification is used to predict the output into a group of classes.
For example, Is it Hot or Cold tomorrow?
Whereas, regression is used to predict the relationship that data represents.
For example, What is the temperature tomorrow?
Advanced Machine Learning Questions
1. What is F1 score? How would you use it?
Let’s have a look at this table before directly jumping into the F1 score.
| Prediction | Predicted Yes | Predicted No |
|---|---|---|
| Actual Yes | True Positive (TP) | False Negative (FN) |
| Actual No | False Positive (FP) | True Negative (TN) |
In binary classification we consider the F1 score to be a measure of the model’s accuracy. The F1 score is a weighted average of precision and recall scores.
F1 = 2TP/2TP + FP + FN
We see scores for F1 between 0 and 1, where 0 is the worst score and 1 is the best score.
The F1 score is typically used in information retrieval to see how well a model retrieves relevant results and our model is performing.
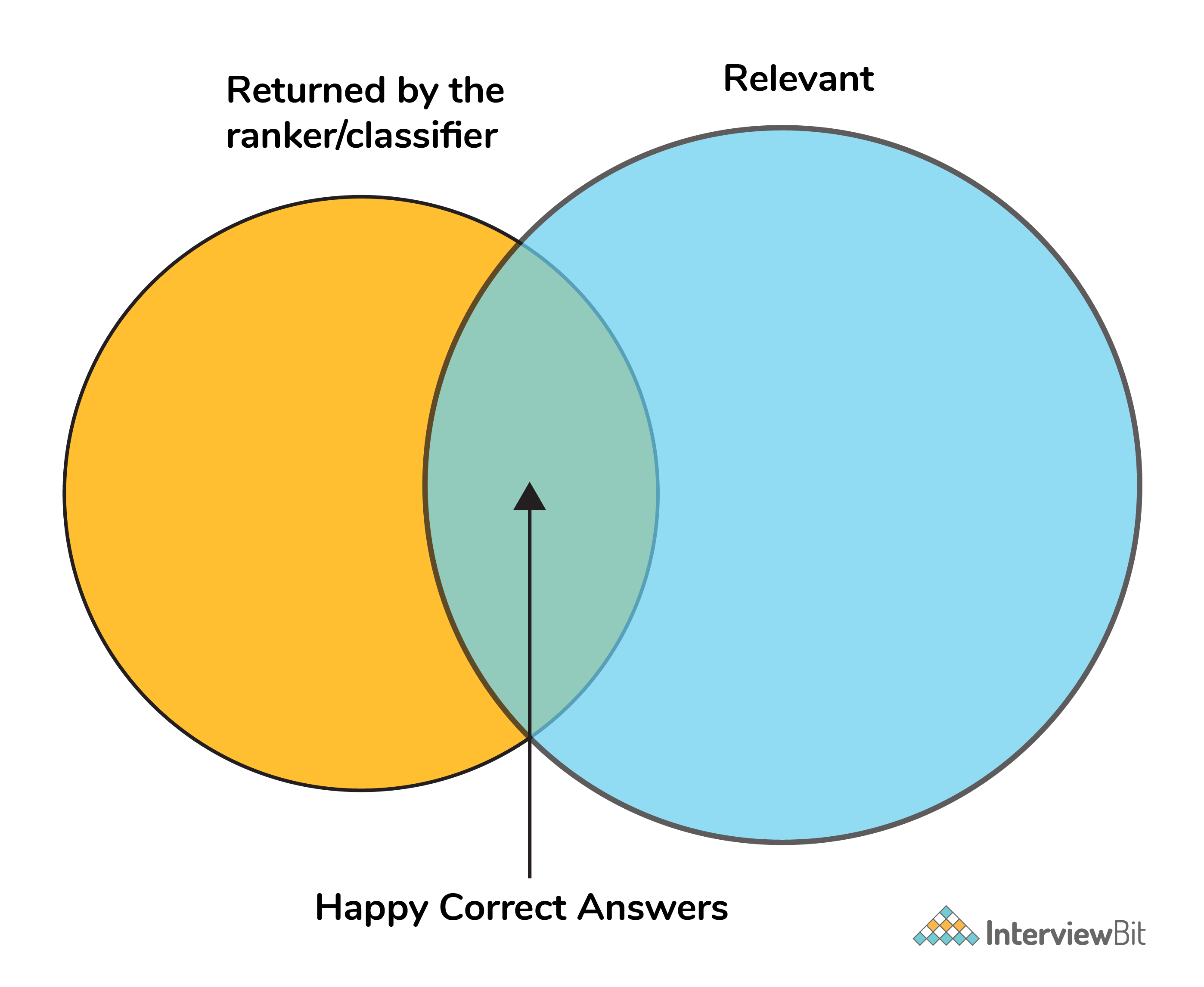
2. Define Precision and Recall?
Precision and recall are ways of monitoring the power of machine learning implementation. But they often used at the same time.
Precision answers the question, “Out of the items that the classifier predicted to be relevant, how many are truly relevant?”
Whereas, recall answers the question, “Out of all the items that are truly relevant, how many are found by the classifier?
In general, the meaning of precision is the fact of being exact and accurate. So the same will go in our machine learning model as well. If you have a set of items that your model needs to predict to be relevant. How many items are truly relevant?
The below figure shows the Venn diagram that precision and recall.
Mathematically, precision and recall can be defined as the following:
precision = # happy correct answers/# total items returned by ranker
recall = # happy correct answers/# total relevant answers
3. How to Tackle Overfitting and Underfitting?
Overfitting means the model fitted to training data too well, in this case, we need to resample the data and estimate the model accuracy using techniques like k-fold cross-validation.
Whereas for the Underfitting case we are not able to understand or capture the patterns from the data, in this case, we need to change the algorithms, or we need to feed more data points to the model.
4. What is a Neural Network?
It is a simplified model of the human brain. Much like the brain, it has neurons that activate when encountering something similar.
The different neurons are connected via connections that help information flow from one neuron to another.
5. What are Loss Function and Cost Functions? Explain the key Difference Between them?
When calculating loss we consider only a single data point, then we use the term loss function.
Whereas, when calculating the sum of error for multiple data then we use the cost function. There is no major difference.
In other words, the loss function is to capture the difference between the actual and predicted values for a single record whereas cost functions aggregate the difference for the entire training dataset.
The Most commonly used loss functions are Mean-squared error and Hinge loss.
Mean-Squared Error(MSE): In simple words, we can say how our model predicted values against the actual values.
Hinge loss: It is used to train the machine learning classifier, which is
L(y) = max(0,1- yy)
Where y = -1 or 1 indicating two classes and y represents the output form of the classifier. The most common cost function represents the total cost as the sum of the fixed costs and the variable costs in the equation y = mx + b
6. What is Ensemble learning?
Ensemble learning is a method that combines multiple machine learning models to create more powerful models.
There are many reasons for a model to be different. Few reasons are:
- Different Population
- Different Hypothesis
- Different modeling techniques
When working with the model’s training and testing data, we will experience an error. This error might be bias, variance, and irreducible error.
Now the model should always have a balance between bias and variance, which we call a bias-variance trade-off.
This ensemble learning is a way to perform this trade-off.
There are many ensemble techniques available but when aggregating multiple models there are two general methods:
- Bagging, a native method: take the training set and generate new training sets off of it.
- Boosting, a more elegant method: similar to bagging, boosting is used to optimize the best weighting scheme for a training set.
7. How do you make sure which Machine Learning Algorithm to use?
It completely depends on the dataset we have. If the data is discrete we use SVM. If the dataset is continuous we use linear regression.
So there is no specific way that lets us know which ML algorithm to use, it all depends on the exploratory data analysis (EDA).
EDA is like “interviewing” the dataset; As part of our interview we do the following:
- Classify our variables as continuous, categorical, and so forth.
- Summarize our variables using descriptive statistics.
- Visualize our variables using charts.
Based on the above observations select one best-fit algorithm for a particular dataset.
8. How to Handle Outlier Values?
An Outlier is an observation in the dataset that is far away from other observations in the dataset. Tools used to discover outliers are
- Box plot
- Z-score
- Scatter plot, etc.
Typically, we need to follow three simple strategies to handle outliers:
- We can drop them.
- We can mark them as outliers and include them as a feature.
- Likewise, we can transform the feature to reduce the effect of the outlier.
9. What is a Random Forest? How does it work?
Random forest is a versatile machine learning method capable of performing both regression and classification tasks.
Like bagging and boosting, random forest works by combining a set of other tree models. Random forest builds a tree from a random sample of the columns in the test data.
Here’s are the steps how a random forest creates the trees:
- Take a sample size from the training data.
- Begin with a single node.
- Run the following algorithm, from the start node:
- If the number of observations is less than node size then stop.
- Select random variables.
- Find the variable that does the “best” job of splitting the observations.
- Split the observations into two nodes.
- Call step `a` on each of these nodes.
10. What is Collaborative Filtering? And Content-Based Filtering?
Collaborative filtering is a proven technique for personalized content recommendations. Collaborative filtering is a type of recommendation system that predicts new content by matching the interests of the individual user with the preferences of many users.
Content-based recommender systems are focused only on the preferences of the user. New recommendations are made to the user from similar content according to the user’s previous choices.

11. What is Clustering?
Clustering is the process of grouping a set of objects into a number of groups. Objects should be similar to one another within the same cluster and dissimilar to those in other clusters.
A few types of clustering are:
- Hierarchical clustering
- K means clustering
- Density-based clustering
- Fuzzy clustering, etc.
12. How can you select K for K-means Clustering?
There are two kinds of methods that include direct methods and statistical testing methods:
- Direct methods: It contains elbow and silhouette
- Statistical testing methods: It has gap statistics.
The silhouette is the most frequently used while determining the optimal value of k.
13. What are Recommender Systems?
A recommendation engine is a system used to predict users’ interests and recommend products that are quite likely interesting for them.
Data required for recommender systems stems from explicit user ratings after watching a film or listening to a song, from implicit search engine queries and purchase histories, or from other knowledge about the users/items themselves.
14. How do check the Normality of a dataset?
Visually, we can use plots. A few of the normality checks are as follows:
- Shapiro-Wilk Test
- Anderson-Darling Test
- Martinez-Iglewicz Test
- Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test
- D’Agostino Skewness Test
15. Can logistic regression use for more than 2 classes?
No, by default logistic regression is a binary classifier, so it cannot be applied to more than 2 classes. However, it can be extended for solving multi-class classification problems (multinomial logistic regression)
16. Explain Correlation and Covariance?
Correlation is used for measuring and also for estimating the quantitative relationship between two variables. Correlation measures how strongly two variables are related. Examples like, income and expenditure, demand and supply, etc.
Covariance is a simple way to measure the correlation between two variables. The problem with covariance is that they are hard to compare without normalization.
17. What is P-value?
P-values are used to make a decision about a hypothesis test. P-value is the minimum significant level at which you can reject the null hypothesis. The lower the p-value, the more likely you reject the null hypothesis.
18. What are Parametric and Non-Parametric Models?
Parametric models will have limited parameters and to predict new data, you only need to know the parameter of the model.
Non-Parametric models have no limits in taking a number of parameters, allowing for more flexibility and to predict new data. You need to know the state of the data and model parameters.
19. What is Reinforcement Learning?
Reinforcement learning is different from the other types of learning like supervised and unsupervised. In reinforcement learning, we are given neither data nor labels. Our learning is based on the rewards given to the agent by the environment.
20. Difference Between Sigmoid and Softmax functions?
The sigmoid function is used for binary classification. The probabilities sum needs to be 1. Whereas, Softmax function is used for multi-classification. The probabilities sum will be 1.
Conclusion
The above-listed questions are the basics of machine learning. Machine learning is advancing so fast hence new concepts will emerge. So to get up to date with that join communities, attend conferences, read research papers. By doing so you can crack any ML interview.
Additional Resources
- Practice Coding
- Best Machine Learning Courses
- Best Data Science Courses
- Free Deep Learning Course with Certification
- Python Interview Questions
- AI MCQs
- Machine Learning Engineer: Career Guide
- Deep Learning Interview
- Machine Learning Engineer Salary
- Machine Learning Vs Data Science
- Machine Learning Vs Deep Learning
- Difference Between Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning












 Download PDF
Download PDF







 Popular
Popular
 5
5
 Enrolled: 6764
Enrolled: 6764














